Understanding the Link: How Climate Change Fuels Extreme Weather Events
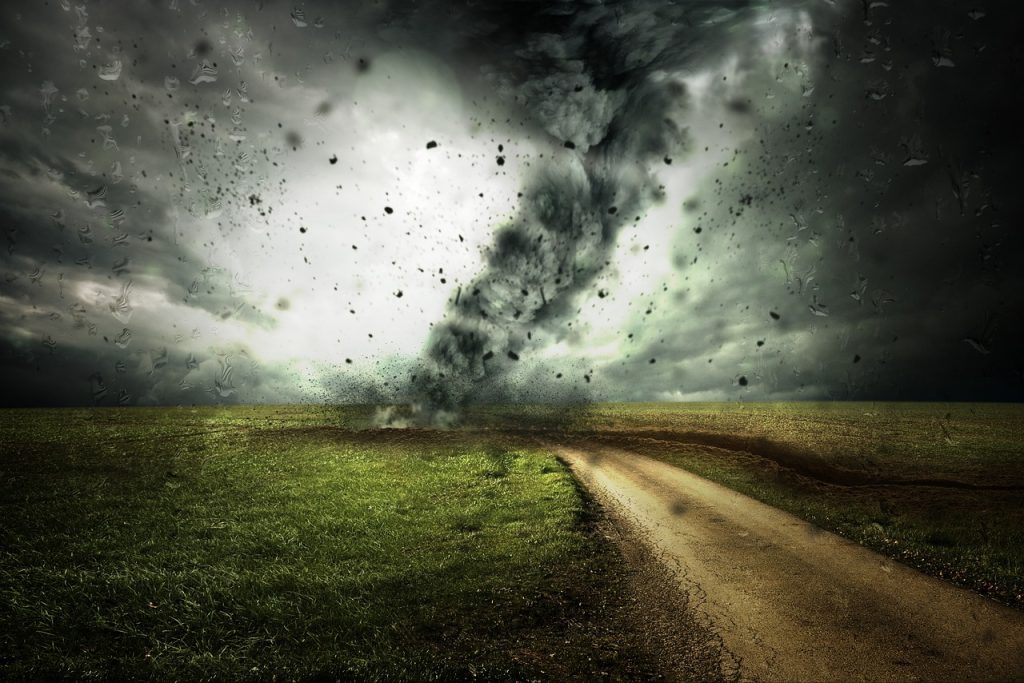
In recent years, the frequency and severity of extreme weather events have noticeably increased, affecting millions globally. From devastating hurricanes and floods to unprecedented heatwaves and droughts – the spike in these events raises significant concerns. But what’s behind this surge in extreme weather occurrences? Today, we delve deep into Understanding the Link: How Climate Change Fuels Extreme Weather Events, a critical topic that underscores the urgent need for environmental sustainability and proactive climate policies.
Introduction to Climate Change and Extreme Weather
Climate change refers to significant changes in global temperatures and weather patterns over time. While climate variability is a natural part of the Earth’s history, the last century has seen an unprecedented rise in global temperatures due to human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas. This increase in temperature is intricately linked to more frequent and severe weather events, a phenomenon that cannot be overlooked.
How Does Climate Change Influence Weather Patterns?
The essence of understanding the link between climate change and extreme weather events lies in the effect of increased global temperatures on weather patterns. Here are a few ways climate change is making its impact felt:
-
Higher Temperatures, Bigger Storms: As global temperatures climb, so does the amount of evaporation from the Earth’s surface, leading to more moisture in the atmosphere. This excess moisture fuels more powerful storms, which explains why hurricanes and tropical storms have become more intense over the decades.
-
Warming Oceans and Rising Sea Levels: The oceans absorb about 90% of the increased atmospheric heat resulting from greenhouse gases. Warmer oceans contribute to more powerful tropical storms and hurricanes. Additionally, as sea levels rise, coastal areas become more susceptible to devastating storm surges and flooding.
-
Droughts and Wildfires: Not all effects of climate change lead to more precipitation. Some areas experience less rainfall and higher temperatures, leading to severe droughts. Drought-stricken areas are more vulnerable to wildfires, which have become larger and more disastrous in regions like Australia, the Amazon, and the western United States.
-
Changing Jet Streams: The jet streams, major air currents in the atmosphere that influence weather patterns, are also affected by the warming of the Arctic. These changes can lead to prolonged weather conditions, such as heatwaves or cold spells, significantly impacting agriculture, health, and the environment.
Real-World Examples of Climate Change Impacting Extreme Weather
Recent events underscore the importance of understanding how climate change fuels extreme weather events. In 2022, Hurricane Ian, a Category 4 storm, brought catastrophic damages to Western Florida, showcasing increased storm intensity. Similarly, the unprecedented European heatwave in the summer of 2023 broke numerous temperature records and was directly linked to human-induced climate warming.
FAQs on Climate Change and Extreme Weather Events
Q1: Can we directly blame climate change for all extreme weather events?
A1: While not all extreme weather can be directly attributed to climate change, the overall increase in the frequency and intensity of these events is strongly connected to global warming and climate variability influences.
Q2: What can individuals do to help mitigate climate change?
A2: Individuals can reduce their carbon footprint by adopting renewable energy sources, conserving energy, reducing waste, and supporting policies and leaders committed to climate action.
Q3: Are certain regions more vulnerable to climate-related weather events?
A3: Yes, geographic and socio-economic factors make certain regions, especially low-lying island nations and densely populated coastal areas, more susceptible to the effects of climate change such as rising sea levels and hurricanes.
Q4: How is climate change affecting biodiversity through extreme weather events?
A4: Extreme weather events like wildfires, floods, and hurricanes can destroy habitats, endanger species, and disrupt ecosystems. The rapid change in climate conditions can also outpace the ability of many species to adapt.
Conclusion: Understanding the Link and Taking Action
Understanding the Link: How Climate Change Fuels Extreme Weather Events is crucial not just for policymakers and scientists but for everyone. As our climate continues to change, the frequency and severity of extreme weather events are likely to increase, posing significant challenges to our readiness and response strategies. By acknowledging these links and understanding the science behind them, we position ourselves to take meaningful steps toward mitigating climate change and protecting our planet for future generations. The time for action is now, and it begins with awareness and understanding.